The Video Game Project
A Closer Look At The Prototypes That Became Your Favourite Games!
Super Nintendo Prototype, Debug & Sample Hardware
 The Super Nintendo Entertainment System or S.N.E.S. for short is a 16-bit home video game console developed by Nintendo. It was released in 1990 in Japan, 1991 in North America, 1992 in Europe and Australasia (Oceania), and 1993 in South America. In Japan, the system is called the Super Famicom (SFC).
The Super Nintendo Entertainment System or S.N.E.S. for short is a 16-bit home video game console developed by Nintendo. It was released in 1990 in Japan, 1991 in North America, 1992 in Europe and Australasia (Oceania), and 1993 in South America. In Japan, the system is called the Super Famicom (SFC).
To compete with the popular Family Computer in Japan, NEC Home Electronics launched the PC Engine in 1987, and Sega followed suit with the Mega Drive in 1988. The two platforms were later launched in North America in 1989 as the TurboGrafx-16 and the Sega Genesis, respectively. Both systems were built on 16-bit architectures and offered improved graphics and sound over the 8-bit NES. Nintendo executives were in no rush to design a new system, but they reconsidered when they began to see their dominance in the market slipping.
It was Nintendo's second home console, following the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) and was designed by Masayuki Uemura, who also designed the original Famicom. The SNES incorporates a Ricoh 5A22 CPU, which is a modification of the WDC 65C816. This has an 8-bit data bus and two address buses. The 24-bit "Bus A" is used for general accesses, while the 8-bit "Bus B" is used to access support chip registers such as the video and audio co-processors. The console also contains 128 KB of general-purpose RAM, which is separate from the RAM dedicated to the video and audio subsystems. The SNES relies on it's Picture Processing Unit (PPU) to output video, which consists of two separate but closely tied IC packages. It contains 64 KB of SRAM for storing video data, 544 bytes of object attribute memory (OAM) for storing sprite data, and 256 × 15 bits of color generator RAM (CGRAM) for storing palette data. This CGRAM allows the console to display up to 256 colors, chosen from the 15-bit RGB color space, for a total of 32,768 possible colors. The PPU is clocked by the same signal as the CPU, and generates a pixel every two or four cycles. Eight video modes are available to the programmer including the infamous Mode 7. The audio subsystem, the S-SMP, is a dedicated single chip consisting of an 8-bit CPU, along with a 16-bit DSP, and 64 KB of SRAM. It is designed and produced by Sony for Nintendo and is completely independent from the rest of the system. It's capable of producing stereo sound, composed from 8 voices generated using 16 bit audio samples and various effects such as reverberation.
In lay mans terms the 16-bit design of the SNES incorporates graphics and sound co-processors that perform tiling and simulated 3D effects, a palette of 32,768 colors, and 8-channel ADPCM audio. These base platform features, plus the ability to dramatically extend them all through substantial chip upgrades inside of each cartridge, represent a leap over the 8-bit NES generation and some significant advantages over 16-bit competitors. The machine introduced advanced graphics and sound capabilities compared with other consoles at the time. Additionally, development of a variety of enhancement chips (which were integrated on game circuit boards) helped to keep it competitive in the marketplace.
The Super Famicom was released in Japan on Wednesday, November 21st, 1990 for ¥25,000. It was an instant success. Nintendo's initial shipment of 300,000 units sold out within hours, and the resulting social disturbance led the Japanese government to ask video game manufacturers to schedule future console releases on weekends. The system's release also gained the attention of the Yakuza, leading to a decision to ship the devices at night to avoid repeated robbery. With the Super Famicom quickly outselling its rivals, Nintendo reasserted itself as the dominant leader of the Japanese console market. Nintendo's success was partially due to the retention of most of its key third-party developers, including Capcom, Konami, Tecmo, Square, Koei, and Enix. They were responsible for some amazing games on the system.
A redesigned version of the Super Famicom, called the Super Nintendo was released in limited quantities in North America on August 23rd 1991 for $199.99, with an official nationwide release date of September 9, 1991. A United Kingdom and Ireland release followed in April 1992 for £150, with a German release following a few weeks later.
Approximately 49.1 million Super NES consoles were sold worldwide, with 23.35 million of those units sold in the Americas and 17.17 million in Japan. Although it could not quite repeat the success of the NES, which sold 61.91 million units worldwide, the SNES was the best-selling console of its era.
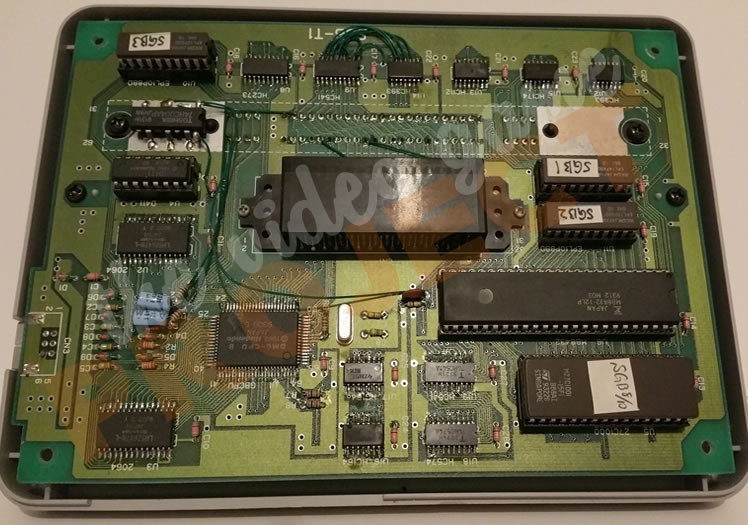
Super Game Boy 2 Prototype
The successor to the Super Game Boy, released exclusively in Japan on January 30, 1998, the Super Game Boy 2 was made as a response to complaints from Japanese Pokémon players who could not trade Pokémon with their friends because they only owned an original Super Game Boy, which lacks a link port.
In terms of features it was very similar to the function of the original Super Game Boy but the outside casing was a much sleeker design, made of transparent blue plastic.
Functionality-wise, a game link port and LED power light were added to the hardware, and the firmware gained 5 new screen border graphics that could be displayed while playing a game. Most notable however, is the addition of an internal oscillator (clock chip) on board, which means the Super Game Boy 2 can run games at the original 59.7 Hz of the original handheld, as opposed to the original Super Game Boy, which lacked its own oscillator and thus ran games at the frequency of the console it was plugged into.
As stated previously, the Super Game Boy 2 was only ever released in Japan but that wasn't always Nintendo's intention. They had originally planned for a US release and this prototype was sent to the west while it was still in devolpment. Because of this it's features differ from the final version.
Further pictures / video of this Super Game Boy 2 prototype in operation will be added as soon as time allows!

SGB 2 - Top

SGB2 - Top Angle

SGB2 - GB PORT
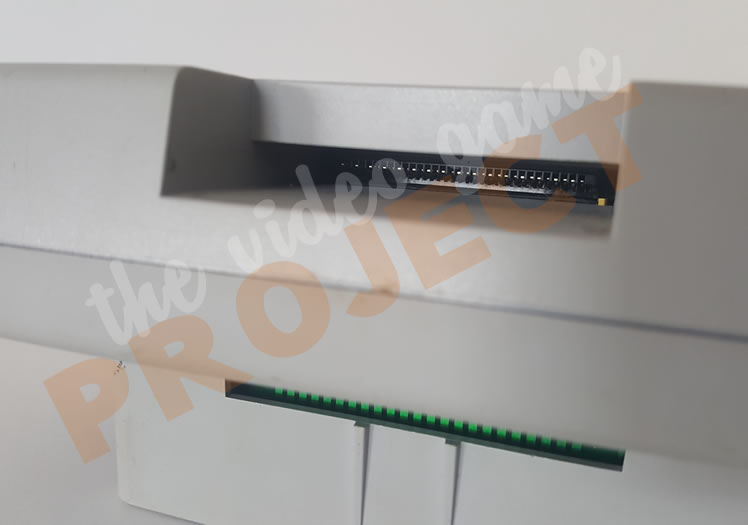

GB Port Alt. View
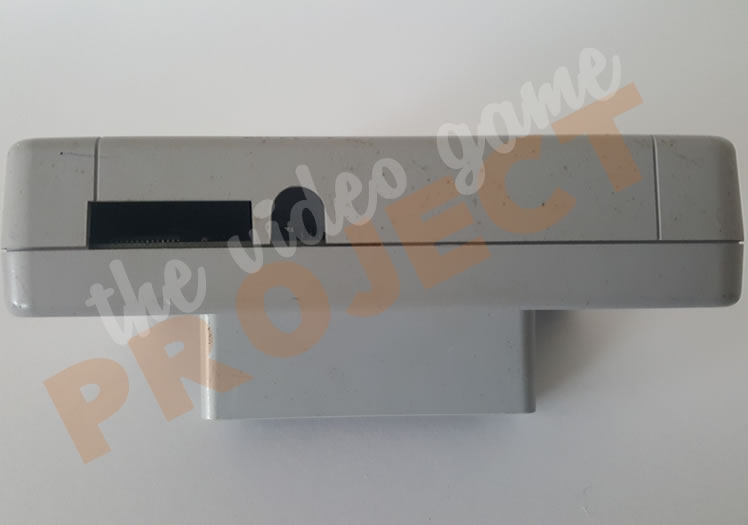

SGB2 - Back
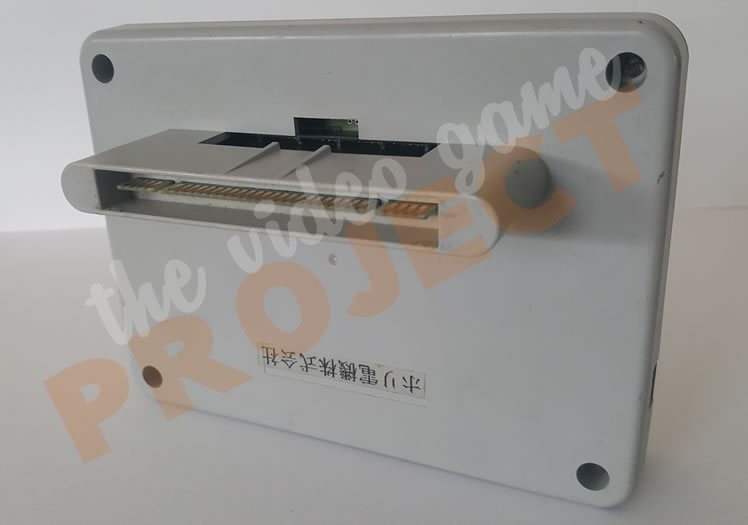

SGB2 - Bottom
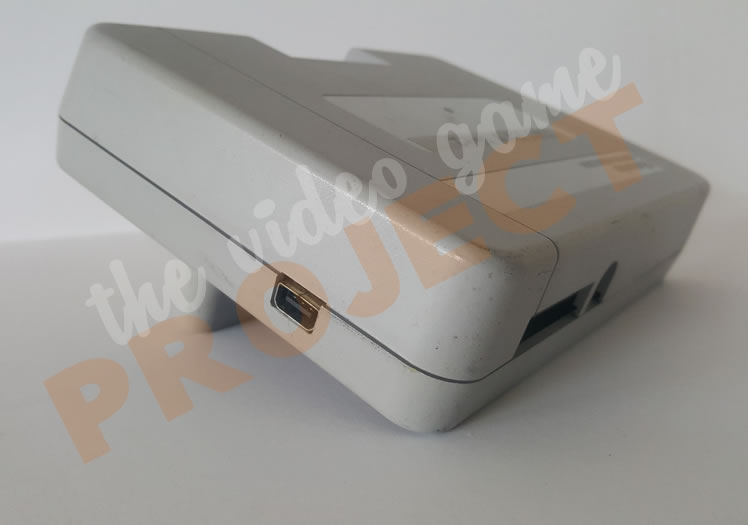

SGB2 - Link Port